Constructivism was introduced by Jean Piaget (1981) and
Bruner (1990). They gave stress to knowledge discovery of new
meaning/concepts/principles in the learning process.
Various strategies have been suggested to foster knowledge
discovery, among these, is making students engaged in gathering unorganized
information from which they can induce ideas and principles.
Students are also asked to apply discovered knowledge to new
situations, a process for making their knowledge applicable to real life
situations.
While knowledge is
constructed by the individual learner in constructivism, knowledge can also be
socially constructed. Social Constructivism is the effort to show that the
construction of knowledge is governed by social, historical and cultural
contexts. In effect, this is to say that the learner who interprets knowledge
has a predetermined point of view according to the social perspectives of the
community or society he lives in.
The psychologist Vygotsky stressed that learning is affected
by social influences. He suggested the interactive process in learning. A more
capable adult (teacher or parent) can aid or complement what the learner sees
in a given tasks or project. In addition, John Dewey sees language as medium
for social coordination and adaptation. For Dewey, human learning is really
human language that occurs when students socially share, build and agree upon
meanings and knowledge.
The Computer’s Capabilities
Informative Tool
The computer can provide vast amounts of information in
various forms, such as text, graphics, sound, and video. Even multimedia encyclopedias
are today available on the internet.
Communication Tool
The computer has been used in communication as evident by
social networking sites as to Facebook, twitter and Friendster. We can even
chat/talk friends and families anywhere in the globe through yahoo messenger or
the one in Facebook or view them through the webcam. We can send messages and
information through the internet in just seconds or minutes.
Constructive Tool
The computer itself can be used for manipulating
information, visualizing one’s understanding, and building new knowledge. The
Microsoft Word computer program itself is desktop publishing software that
allows users to organize and present their ideas in attractive formats.
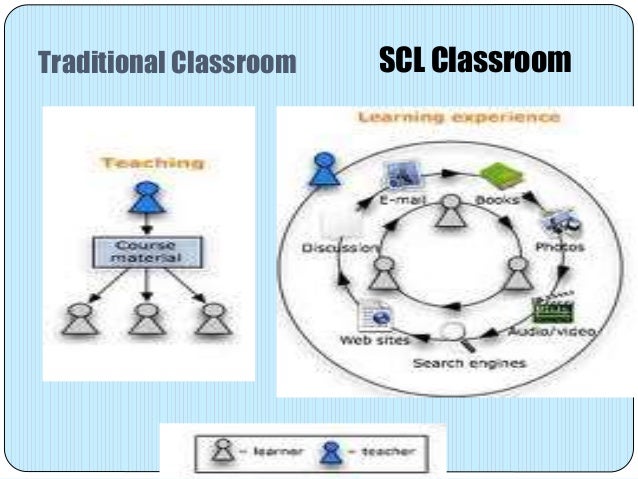
Co-constructive Tool
Students can
use constructive tools to work cooperatively and construct a shared
understanding of new knowledge. One way of co-construction is the use of the
electronic whiteboard where students may post notices to a shared
document/whiteboard. Students may also co-edit the same document from their
homes.
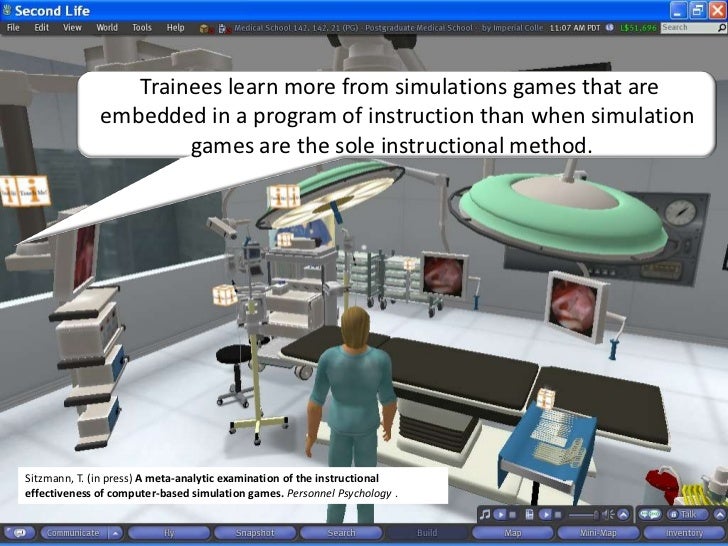
Situating Tool
By means of
virtual reality (RS) extension systems, the computer can create 3-D images on
display to give the user the feeling that are situated in a virtual
environment. A flight simulation program is an example of a situating tool
which places the user in simulated flying environment.




















.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)




